执行的任务(Tasks)
- tasks是从上到下顺序执行,如果中间发生错误,那么整个playbook会中止。你可以改修文件后,再重新执行。
- 每一个task的对module的一次调用。使用不同的参数和变量而已。
- 每一个task最好有name属性,这个是供人读的,没有实际的操作。然后会在命令行里面输出,提示用户执行情况。
语法
task的基本写法:
tasks:
- name: make sure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=running
其中name是可选的,也可以简写成下面的例子。
tasks:
- service: name=httpd state=running
写name的task在playbook执行时,会显示对应的名字,信息更友好、丰富。写name是个好习惯!
TASK: [make sure apache is running] *************************************************************
changed: [yourhost]
没有写name的task在playbook执行时,直接显示对应的task语法。在调用同样的module多次后,不同意分辨执行到哪步了。
TASK: [service name=httpd state=running] **************************************
changed: [yourhost]
参数的不同写法
最上的代码展示了最基本的传入module的参数的方法 key=value
tasks:
- name: make sure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=running
当需要传入参数列表太长时,可以分隔到多行:
tasks:
- name: Copy ansible inventory file to client
copy: src=/etc/ansible/hosts dest=/etc/ansible/hosts
owner=root group=root mode=0644
或者用yml的字典传入参数
tasks:
- name: Copy ansible inventory file to client
copy:
src: /etc/ansible/hosts
dest: /etc/ansible/hosts
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
TASK的执行状态
task中每个action会调用一个module,在module中会去检查当前系统状态是否需要重新执行。
- 如果本次执行了,那么action会得到返回值changed;
- 如果不需要执行,那么action得到返回值ok
module的执行状态的具体判断规则由各个module自己决定和实现的。例如,”copy” module的判断方法是比较文件的checksum,代码如下:
https://github.com/ansible/ansible-modules-core/blob/devel/files/copy.py
状态示例
以一个copy文件的task为例子:
tasks:
- name: Copy the /etc/hosts
copy: src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/hosts
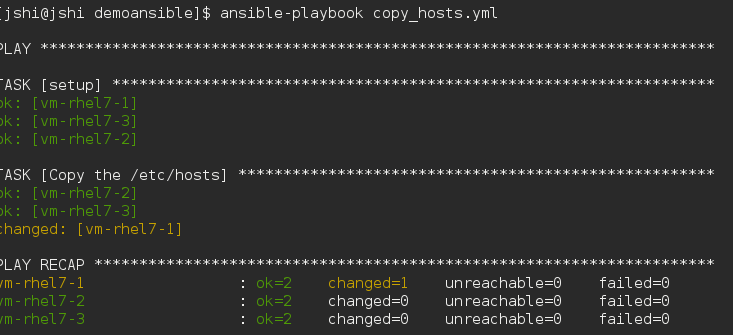
第一次执行,它的结果是这个样子的:
TASK的状态是changed
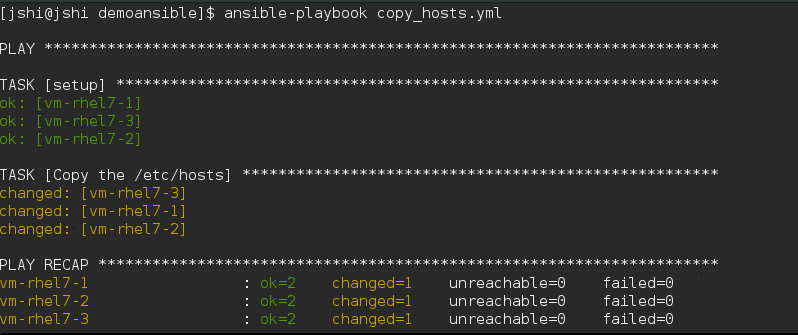
第二次执行是下面这个样子的:
TASK的状态是ok,由于第一次执行copy_hosts.yml的时候,已经拷贝过文件,那么ansible目标文件的状态避免重复执行.

下面我更改vm-rhel7-1的/etc/hosts, 再次执行看看: